On the edit tab in the snapping group enable your snapping preferences.
Rubber sheeting esri.
Rubbersheeting is used to make small geometric adjustments in your data usually to align features with more accurate information.
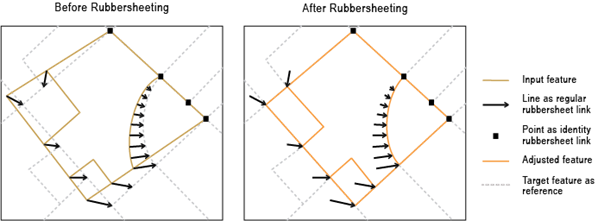
Rubbersheeting makes spatial adjustments to align the input feature locations with more accurate target feature locations based on the specified rubbersheet links.
This exercise will show you how to rubber sheet data by using displacement links multiple displacement links and identity links.
Rubbersheeting is used to make small geometric adjustments in your data usually to align features with more accurate information.
The input link features represent the regular links.
The input point features represent identity links that hold source positions unmoved during the rubbersheeting process.
Rubbersheeting is typically used to align two or more layers.
Rubber sheeting may improve the value of such sources and make them easier to compare to modern maps.
The source layer drawn with solid lines is adjusted to the more accurate target layer.
Editing coverages tables with arcedit the adjust command in the arcedit command reference and understanding gis.
This process moves the features of a layer using a piecewise transformation that preserves straight lines.
For steps to transform features using affine or similarity transformation methods see transform features.
The input point features represent identity links that hold source positions unmoved during the rubbersheeting process.
The source layer drawn with solid lines is adjusted to the more accurate target layer.
In rubbersheeting adjustments you are usually trying to align one layer with another that is often in close proximity.
Esri s arcgis 8 3 has the capability of rubber sheeting vector data and arcmap 9 2 may also rubber sheet raster layers.
Autocad s land desktop allows a user to rubber sheet raster data.
Rubber sheeting is commonly used after a transformation to further refine the alignment accuracy of the transformed features.
The following is a summary of the command sequence that should be used when rubber sheeting two or more coverages.
Rubbersheeting makes spatial adjustments to align the input feature locations with more accurate target feature locations based on the specified rubbersheet links.
Esri s arcgis 8 3 has the capability of rubbersheeting vector data and arcmap 9 2 may also rubber sheet raster layers.
For conceptual and detailed usage information refer to.